The Internet is the last place to share very personal information. Among the reasons for this are the prevention of scams aimed at hacking online accounts and stealing money from the victim, in addition to preserving privacy against the abuse of companies that exploit data commercially. In some cases, a simple photo posted on social media can serve to unravel the habits of a family and make them the target of scams. In the following list, check out eight types of information that should never be made public on the web.
READ: Porn scam has already stolen R $ 440 thousand from victims; Look

Bank data is among information that should never be shared on the Internet Photo: Pond5
Want to buy cell phones, TV and other discounted products? Meet Compare dnetc
Never share your bank details on social media, even if it is just the name of the bank, the branch and the account number. As much as this is not enough to hack into a bank account, this information can be used to fake e-mails and correspondence as a way to trick the victim into delivering more data or paying a fake bill with money that will end up in the account of the criminal.
The same goes for shopping sites. If a store does not have HTTPS or a security seal, any information entered there may be misplaced and used in a future scam. Do not make payments by transfer unless you trust the site and are using a virus-free PC and a secure network, such as your own home Wi-Fi.

Do not enter financial data on suspicious sites Photo: Pond5
Avoid disclosing your company name, address, position and other details about your work online. This type of information can be used by criminals in various scams based on identity theft. This year, hackers used artificial intelligence software to mimic the voice of a British company's CEO and to order bank transfers. This type of crime, regardless of the level of sophistication, is more difficult to happen when the target's professional data is not public.
The location is one of the main weaknesses of security. On the Internet, it is important to click Block whenever a website wants to track the position using Wi-Fi data or, in the case of a cell phone, also GPS. Deliver the information only if it is crucial to the functioning of the service, as in the case of map applications.
On social networks, avoid posting check-ins to your entire contact network. In addition, an option to revoke access to your location for apps such as Facebook, Instagram and Twitter, even if the geolocation function of photos does not work properly.
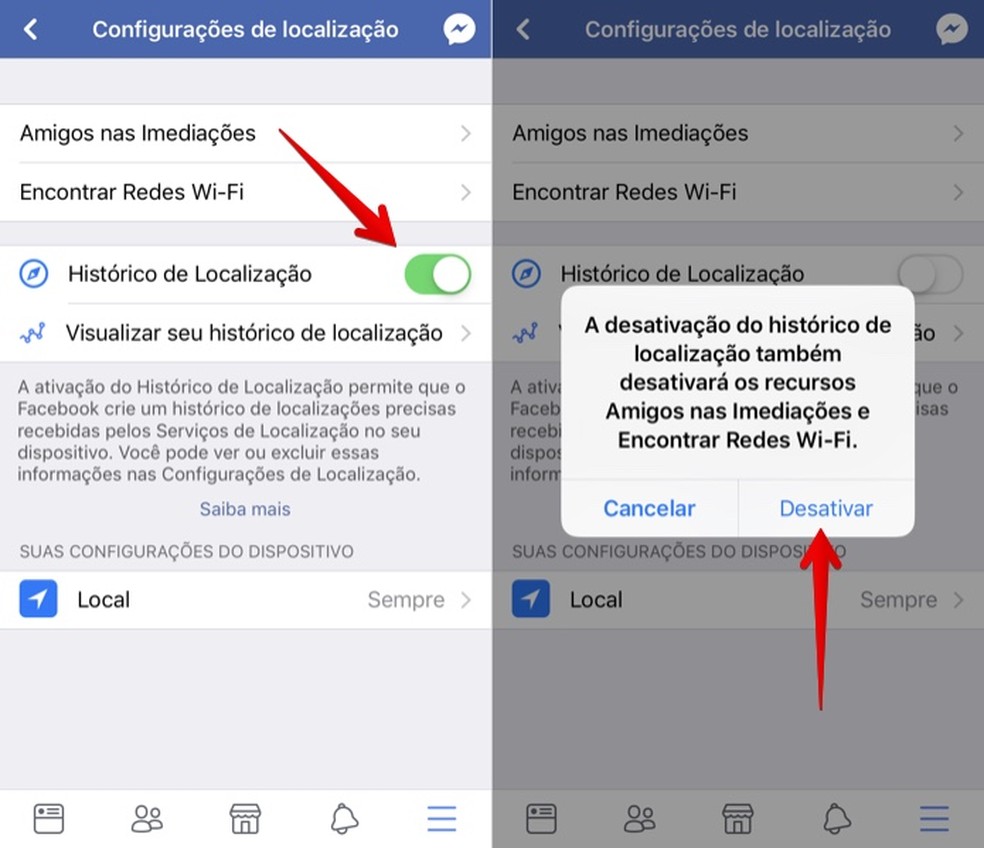
Prevent Facebook from tracking your location Photo: Reproduo / Helito Bijora
4. Information about children and routine
Avoid posting photos, name and address of the children's school and other information about the family's routine. A simple image can serve to identify the place where the child studies, departure and arrival times, among other details that facilitate strokes and even kidnappings. The same goes for holidays and trips: never publicly say the days when the house is empty.
This data can easily be obtained when posting on social media. When posting photos, always prefer to filter who can see them on Facebook and still use Instagram's best friends list, but be aware that there is always some risk involved.
Avoid filling social media profiles with all your personal data. Do not include your address or phone number, or leave it marked "Only you" so that you are not exposed to anyone. If you also don’t have confidence in the developer of a mobile app, do not allow sharing your mobile phone number or contact list if requested.
Exposed information can fall into the hands of criminals and facilitate scams involving, for example, hiring services that require little or no identity verification, such as cell phone and TV plans.

Do not disclose address and phone on social networks Photo: Reproduo / Paulo Alves
6. Photos of personal documents
Photos of ID, driver's license, passport and other documents should never be posted online. With this information in hand, criminals can apply more sophisticated scams that even involve opening bank accounts (to receive theft money) and apply for loans. Avoid even publishing images of the closed passport: on the cover, it is possible to know if the document is due for five or 10 years, or if the person has foreign citizenship.
7. Photos of tickets, tickets and air tickets
Never post a photo of anything on the Internet that contains a barcode or similar. This type of information can be used to falsify tickets, bus and train tickets or air tickets just by the image. Only with the photo of the boarding pass, it is possible to obtain the digital version in an application and even discover the flight data, such as location and time, in addition to the passenger's first and last name.
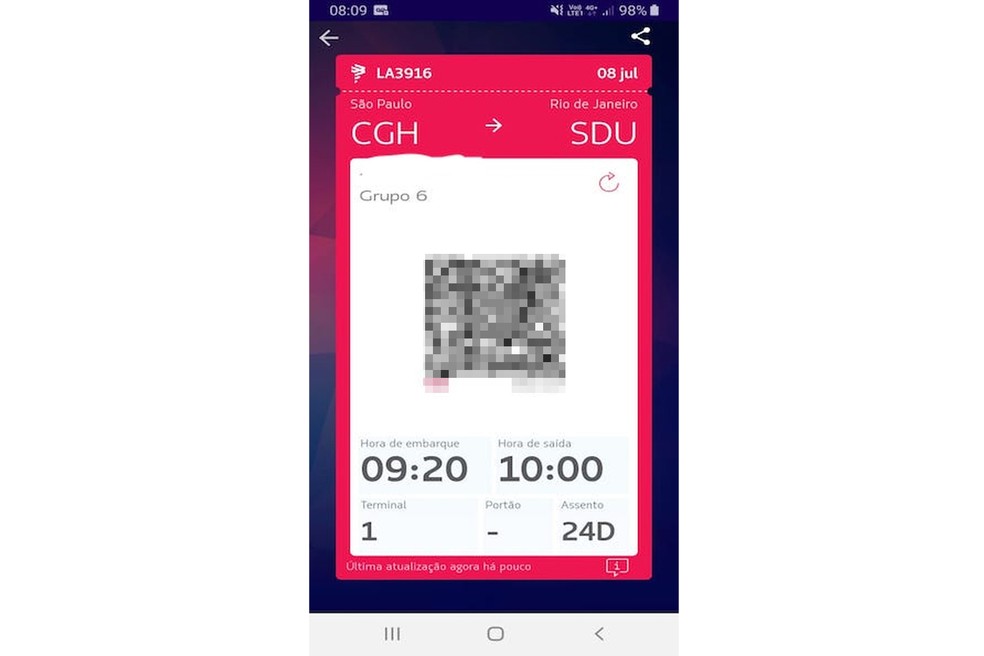
Airline applications can reveal flight and passenger data using the barcode Photo: Reproduo / Sara Faria

Google Maps has unusual functions that can make your life easier
