BERT is the new search algorithm behind searches performed through Google. The new tool uses artificial intelligence to understand the user's requests, based on a construction of meaning that takes into account the context of each word and phrase. Thus, the search engine can offer more accurate results and focused on what really interests the person. The technology is already applied in versions from 70 countries, including Brazil, of Google's search service.
READ: Google reveals the most searched subjects in Brazil in 2019

Google search technology gains reinforcement of new artificial intelligence Photo: Marvin Costa / dnetc
The term algorithm has its origins in mathematics and, from the point of view of computer science, it serves to classify a set of steps that a certain software needs to perform to reach a result.
In the case of a search algorithm, and in a simplified way, these steps could be to capture the text that the user enters in the search box and search the Internet for results that are then displayed on the screen. Generally speaking, when someone cites Google's search algorithm (or any algorithm, really), they are referring to a software engine that performs a specific task.
Before applying the new algorithm, Google searches gave more relevance to keywords than to the context of questions. In addition, they organized the results giving more evidence to the most accessed content: that is why, sometimes, when searching for doubts about a product, you can be directed to online stores before finding the information that really matters.
These results, created by the relevance and importance of the keywords, lead to inconsistencies, especially in a scenario in which 15% of all searches performed per day are completely unrelated. As they were never done, the previous algorithm did not have good parameters for organizing the answers, deepening the problem of inaccuracy of the results.
Regarding the search itself, the algorithm processed word for word independently and this created a habit for users. According to Google, the tendency for people to do searches only using the keywords they consider important, without building a question with a beginning, middle and end is something that Google believes is not only possible, but desirable, for the better. results with BERT.
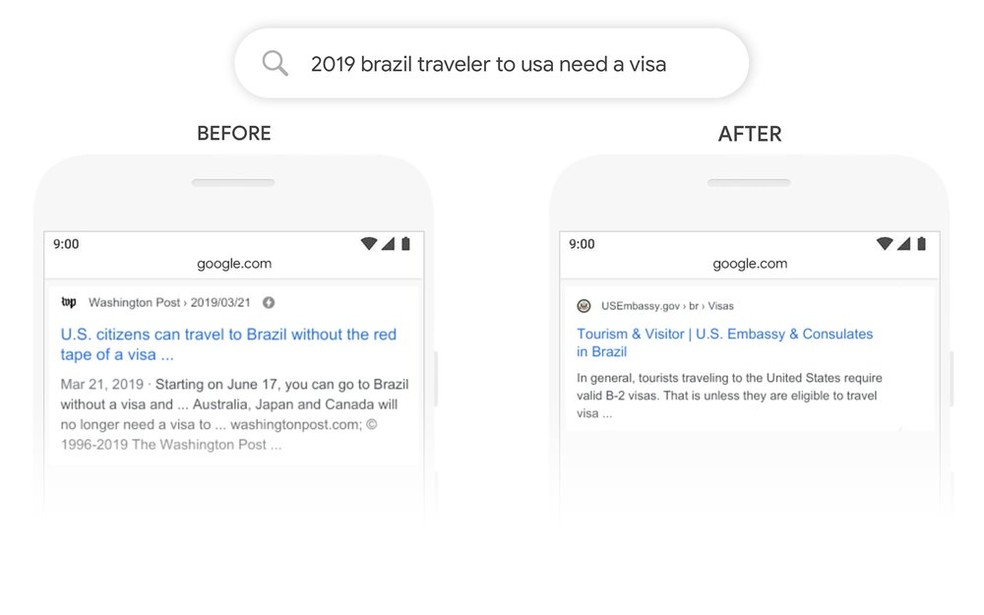
left, without BERT. right, the most accurate result with the help of the algorithm Foto: Divulgao / Google
The image above compares the results of the same search with or without BERT. The question, in free translation: "2019 traveler Brazil to USA needs a visa". Without BERT, Google gives a first response to a news item from the Washington Post whose title "American citizens can travel to Brazil without documentation or visa", which is exactly the opposite of what was sought.
With BERT, the algorithm takes the phrase formulation into context and realizes that the search is linking Brazil as a starting point and the United States as a destination, which gives a more accurate result: the website of the US Embassy in Brazil .
The idea behind BERT is to offer a search tool that does not give much weight to keywords, but rather to the context of searches. Thus, he tries to infer the real meaning of the research and offer results that are more in line with what the person is actually researching. The tool is a complement to that of RankBrain, the first artificial intelligence technique associated with search results and implemented by Google five years ago.
To that end, Google trained the tool with texts extracted from Wikipedia articles. With this database in hand, Google's developers started training AI with completion tests, similar to those that children perform in the literacy phase: snippets of text had words removed and the algorithm needed to find the ideal term to complete the content, without harming its meaning.
With this, BERT should enable more accurate and more contextual results to the Google search engine. This ability tends to deepen the quality of the tool, since it is common that the user simply does not know exactly how to formulate a search correctly. As Google notes on its official blog, we often use search engines to learn something new that we don't know how to search for efficiently.
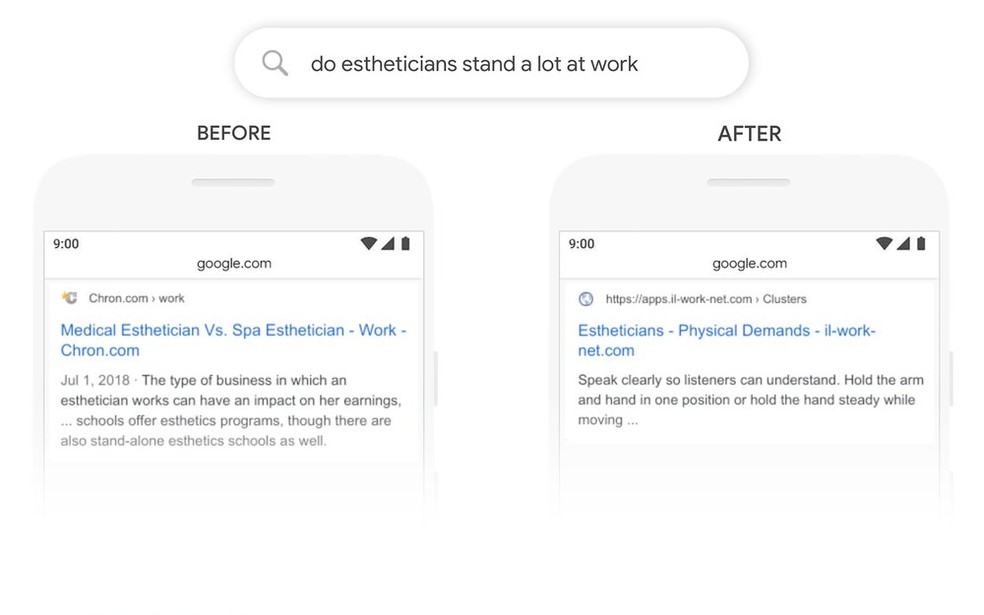
Comparison shows difference in results between algorithms Photo: Divulgao / Google
In the image, another comparison. The search for "beauticians can handle a lot at work". Without BERT, the result is a comparison between two types of professionals. J with BERT the most relevant answer: the result points to a website that details what are the demands that are part of the professional routine of a beautician.
Another development of technology has to do with voice assistants and speech searches. According to Google, the application of BERT's more contextual processing should allow users to interact more naturally with voice assistants, since the algorithm must be able to better understand the directions of the instructions.
How do I update Google Play Services on my phone? Find out in the dnetc Forum

How to delete recent Google searches on mobile
